Proton Therapy
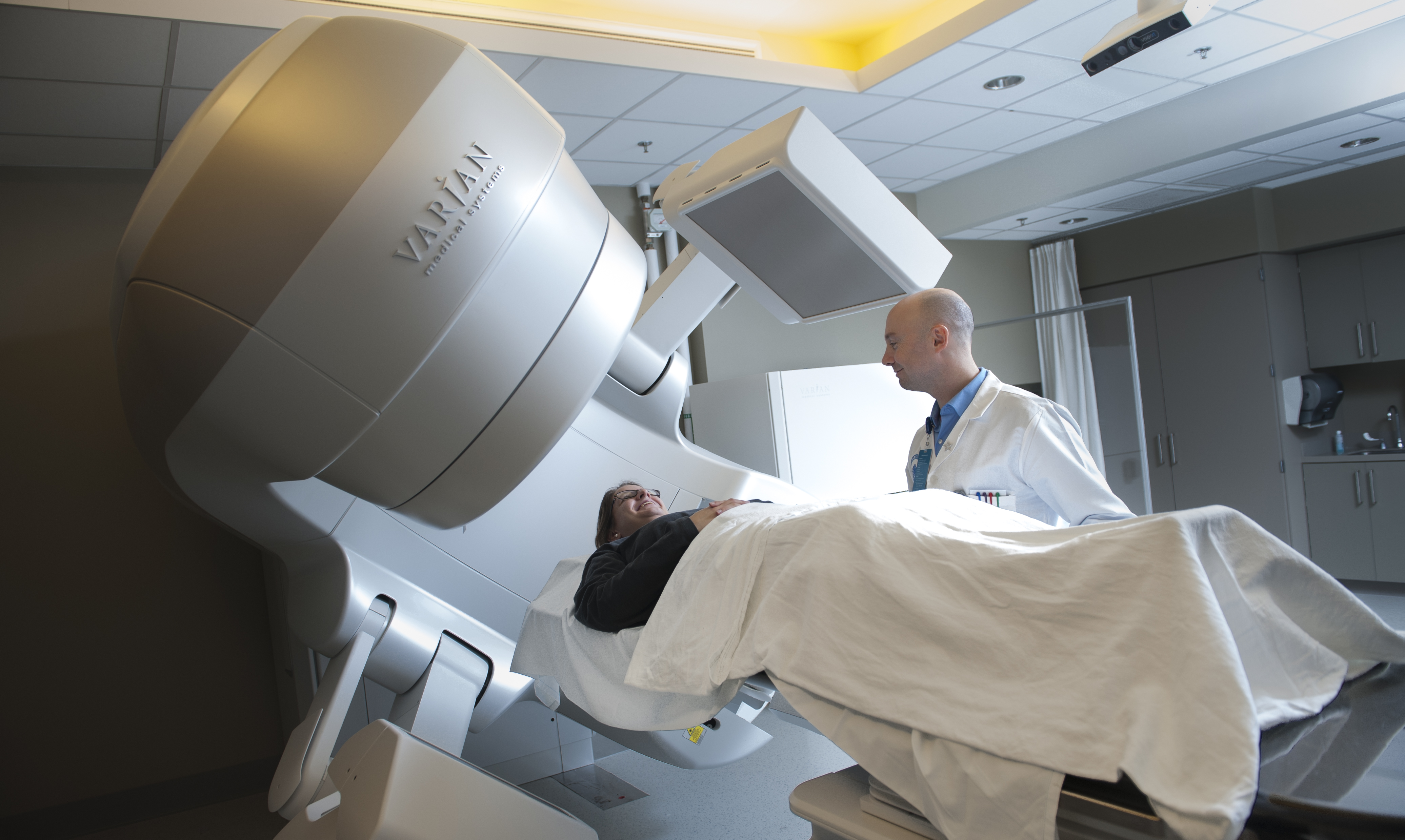
The Francis H. Burr Proton Therapy Center at Massachusetts General Hospital was opened in 2001 and has treated more than 10,000 patients. The facility relies upon an IBA cyclotron and delivers the treatment beam to two 360o gantries and a dedicated ocular treatment line. Before 2001, patients were treated with protons at the Harvard Cyclotron Laboratory across the river at Harvard University.
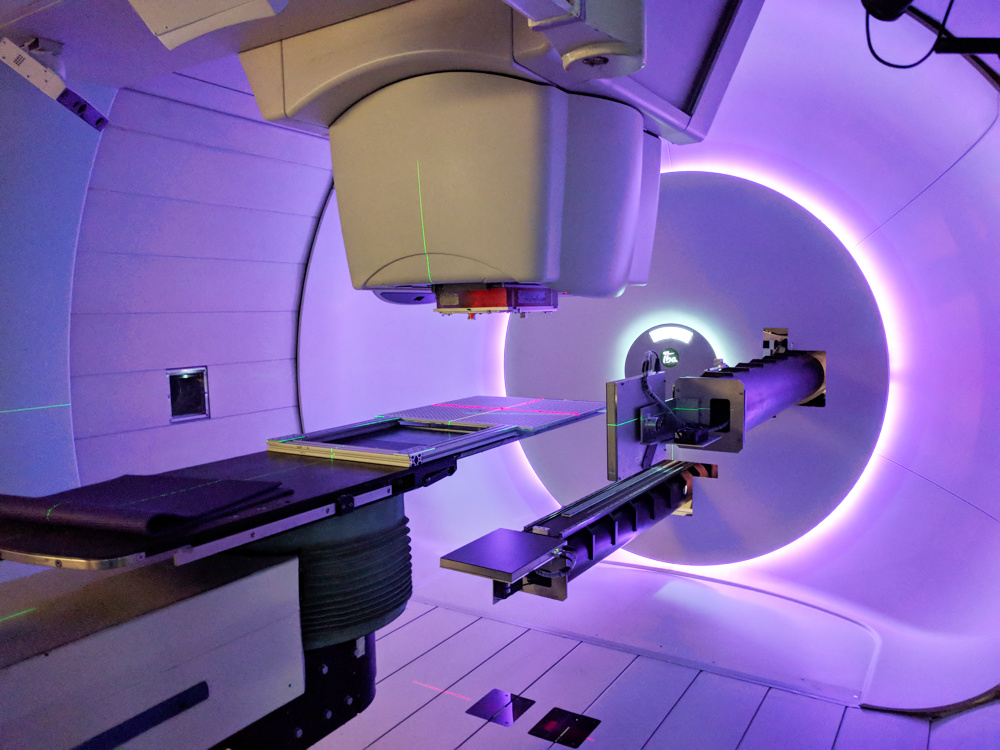
The Gordon Browne Proton Therapy Center has been in operation since February 2020 and is housed in the Lunder Building next to the photon clinic. It is a compact facility that features a robotic patient positioner, cone beam CT and orthogonal X-ray imaging, a pencil beam scanning nozzle, a 70 to 330 MeV synchrotron accelerator, and a gantry that rotates the nozzle through 190 degrees. The combination of these technologies enables 3-dimensional imaging of the patient, movement of a precise point within the patient to the treatment area, and the delivery of one or more highly-conformal beams that intersect the target volume. The facility has 3-dimensional electronic control of the dose without the need of patient specific hardware and rotating beam degraders. The lateral dose distribution is controlled by 2-dimensional magnetic scanning of individual proton pencil beams and the longitudinal dose distribution is controlled by synchrotron electromagnets.
Click here to learn more about proton therapy at Mass General.
The Francis H. Burr Proton Therapy Center
The Gordon Browne Proton Therapy Center
Photon Therapy
The Department of Radiation Oncology has photon treatment facilities on Mass General's main campus in Boston and community locations (Emerson Hospital, North Shore Center for Outpatient Care, and Newton-Wellesley Hospital). We also have an affiliation with Cooley Dickinson Hospital in western MA.
The main campus provides comprehensive therapeutic radiation services including brachytherapy, intraoperative electron therapy, total body irradiation, frameless cone and MLC-based stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), stereotactic body radiation thearpy (SBRT), and kilovoltage treatments. In 2012, the department relocated most of the photon services into the Lunder Building on the main campus. Six linear accelerators are located in the Lunder Building, with dosimetry offices located on the floor above the treatment rooms. The linacs consist of two Elekta machines with Agility collimators, three Varian TrueBeam machines with respiratory gating capabilities, and one Varian ETHOS with adaptive treatment capability. Treatment planning for all photon machines is performed in RayStation using multicriteria optimization techniques for intensity-modulated treatments. All linacs have cone-beam CT imaging available, and three linacs also have Vision RT surface-guided imaging.
Brachytherapy at the main campus utilizes one Elekta high-dose-rate (HDR) 30-channel microSelectron afterloader in the Cox building with the department’s two CT simulators. HDR procedures performed include gynecologic (vaginal cylinders, tandem, and interstitial), interstitial treatments for prostate and head-and-neck cancers, and surface applicators for diseases of the skin. Low-dose-rate (LDR) seed implants are also performed for prostate cancer, using I-125, and for brain tumor resection, using Cs-131.
Satellite facilities provide the same high-quality care as the main campus in convenient community locations. Each facility has its own CT simulator and the same imaging capabilities as the main campus, including cone-beam CT and Vision RT.